Topics
Living World and Classification of Microbes
Health and Diseases
Force and Pressure
Current Electricity and Magnetism
Inside the Atom
Composition of Matter
- Matter (Substance)
- Characteristics of Particles (Molecules) of Matter
- States of Matter
- The Solid State
- The Liquid State
- The Gaseous State
- Elements
- Earth and Elements
- Non-Metals
- Type of Element: Metalloid
- Compound
- Types of Compound
- Mixture
- Types of Mixtures
- Introduction to Solutions
- Suspension Solution
- Colloidal Solution
- Molecular Formula of Compounds
- Periodic Trends in the Modern Periodic Table
Metals and Nonmetals
Pollution
- Pollution
- Air Pollution
- Prevention and Control of Air Pollution
- Water Pollution
- Effects of Water Pollution
- Prevention and Control of Water Pollution
- Soil Pollution
- Effects of Soil Pollution
- Prevention and Control of Soil Pollution
- Relationship of Soil Pollution with Air and Water Pollution
- Laws for Control, Regulation, and Prevention of Pollution by Indian Government
Disaster Management
Cell and Cell Organelles
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell
- Plant Cell Vs Animal Cell
- Cell Organelles
- Structure of the Cell > Cell Wall: “Supporter and Protector”
- Structure of the Cell > Plasma Membrane / Cell Membrane
- Structure of the Cell > Cytoplasm: “Area of Movement”
- Structure of the Cell > Nucleus: “Brain” of the Cell
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Golgi Apparatus - "The delivery system of the cell"
- Lysosome - “Suicidal Bag”
- Mitochondria - “Power House of the Cell”
- Plastids
- Non-living Substances Or Cell Inclusion
Human Body and Organ System
- Human Body
- Human Organ System
- Mechanism of respiration-Breathing
- Human Respiratory System
- Blood Circulatory System
- Human Heart
- Blood Vessels
- Circulation of Blood in the Heart (Functioning of Heart)
- Heart Beat
- Blood
- Composition of Blood > Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood)
- Composition of Blood > Cellular Elements: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Composition of Blood > Cellular Elements: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Composition of Blood > Cellular Elements: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Functions of Blood
- Blood Transfusion and Blood Groups (ABO and Rh system)
- Blood Pressure (B.P.)
- Heart Related Conditions
Introduction to Acid and Base
Chemical Change and Chemical Bond
Measurement and Effects of Heat
Sound
Reflection of Light
Man Made Materials
Ecosystems
Life Cycle of Stars
- Introduction of Nuclear Reactor
- Components of a Nuclear Reactor
- Heat Removal and Energy Conversion
Introduction of Nuclear Reactor:
A nuclear reactor is a machine that generates large-scale electricity using atomic energy derived from nuclear reactions on nuclear fuel.
Nuclear Fuel Example: Uranium-235,
- When Uranium-235 (U-235) is hit with slow neutrons, its nucleus splits in a process called nuclear fission.
- This fission produces Krypton-92 and Barium-141 nuclei, along with the release of 2 to 3 additional neutrons.
- These released neutrons can cause more U-235 nuclei to undergo fission, creating a chain reaction.


Nuclear fission (Chain reaction)
A chain reaction releases a large amount of nuclear energy. To prevent an explosion, the reaction must be carefully controlled by managing the speed and number of neutrons.
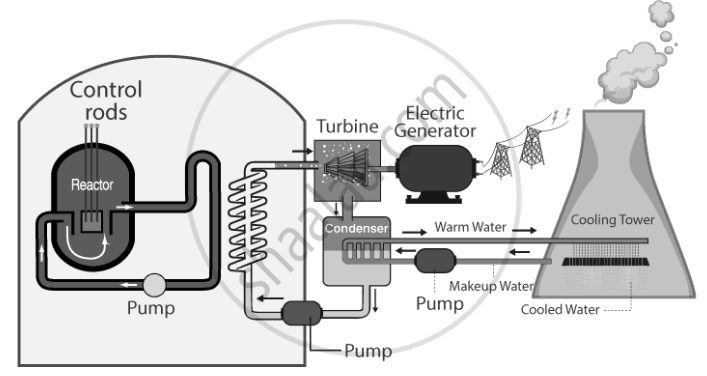
Components of a Nuclear Reactor:
- Core: Holds the nuclear fuel and produces the heat needed for energy generation.
- Nuclear Fuel: The primary material, such as Uranium-235 or Plutonium-239, that undergoes fission to release energy.
- Moderator: Materials like graphite or heavy water are used as moderators to reduce the speed of neutrons and keep the reaction steady.
- Controller: Rods made of boron, cadmium, or beryllium absorb excess neutrons to control the number of neutrons and prevent the chain reaction from escalating.
- Coolant: It circulates through the core, absorbing heat and carrying it to the turbines.
- Turbine: Converts the absorbed heat energy into mechanical energy.
- Cooling Tower: Releases excess heat that cannot be converted or used.
- Containment: A protective structure that isolates the reactor from the environment.

Nuclear reactor: Bhabha Atomic Research centre, Mumbai
Heat Removal and Energy Conversion:
The heat produced during nuclear fission is absorbed by water, which acts as a coolant. The heated water turns into steam, which drives turbines to produce electricity.
Nuclear reactors in India:
India has 22 operational nuclear reactors at eight different locations. The first nuclear reactor in India, named ‘Apsara,’ became critical on 4th August 1956 at the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre in Mumbai.
- India has significant reserves of Thorium-232 (Th-232).
- Indian scientists plan to use Th-232 to produce Uranium-233 (U-233) for future nuclear energy projects.
