Topics
Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry
- Introduction of Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Development of Chemistry
- Importance of Chemistry
- Nature of Matter
- Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter
- Molecules
- Elements
- Compound
- Properties of Matter and Their Measurement
- The International System of Units (SI)
- Mass and Weight
- Laws of Chemical Combination
- Law of Conservation of Matter (Law of Conservation of Mass)
- Law of Constant Proportions (Law of Definite Proportions)
- Law of Multiple Proportions
- Gay Lussac’s Law of Gaseous Volumes
- Avogadro's Law
- Dalton's Atomic Theory
- Atomic and Molecular Masses
- Atomic Mass
- Average Atomic Mass
- Molecular Mass
- Formula Mass
- Mole Concept
- Percentage Composition
- Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations - Introduction
- Concentration of a Solution
- Accuracy, Precision and Uncertainty in Measurement
- Uncertainty in Measurement
- Scientific Notation
- Dimensional Analysis
- Significant Figures
States of Matter
- Classification of Matter
- States of Matter
- The Solid State
- The Liquid State
- The Gaseous State
- Intermolecular Forces - Introduction
- Intermolecular Forces
- Dispersion Forces Or London Forces
- Dipole - Dipole Forces
- Dipole-induced Dipole Forces
- Hydrogen Bond
- Intermolecular Forces Vs. Thermal Interactions
- Gas Laws
- Boyle’s Law (Pressure - Volume Relationship)
- Charles’ Law (Temperature - Volume Relationship)
- Gay Lussac’s Law (Pressure- Temperature Relationship)
- Avogadro's Law
- Ideal Gas Equation
- Density and Molar Mass of a Gaseous Substance
- Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
- Absolute Scale of Temperature
- Kinetic Energy and Molecular Speeds
- Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
- Classification of Gases: Real Gases and Ideal Gases
- Behaviour of Real Gases: Deviation from Ideal Gas Behaviour
- Liquefaction of Gases
- Compressibility Factor
- Van Der Waals Equation
- Vapour Pressure
- Viscosity
- Surface Tension
- States of Matter:- Gases and Liquids Numericals
- General Characteristics of Solid State
- Amorphous and Crystalline Solids
- Classification of Crystalline Solids
- Crystal Lattices and Unit Cells
- Crystal Lattices and Unit Cells - Primitive and Centred Unit Cells
- Number of Atoms in a Unit Cell
- Bragg's Law and Its Applications
- Close Packed Structures of Solids
- Close Packed Structures - Formula of a Compound and Number of Voids Filled
- Packing Efficiency
- Packing Efficiency in hcp and ccp Structures
- Efficiency of Packing in Body-centred Cubic Structures
- Packing Efficiency in Simple Cubic Lattice
- Calculations Involving Unit Cell Dimensions
- Imperfections in Solids - Introduction
- Imperfections in Solids
- Types of Point Defects - Stoichiometric Defects
- Types of Point Defects - Impurity Defects
- Types of Point Defects - Non-stoichiometric Defects
- Properties of Solids: Electrical Properties
- Properties of Solids: Electrical Properties
- Conduction of Electricity in Metals
- Conduction of Electricity in Semiconductors
- Applications of n-type and p-type Semiconductors
- Properties of Solids: Magnetic Properties
- Crystal Structure of Solids
Atomic Structure
- Subatomic Particles
- Discovery of Electron
- Charge to Mass Ratio of Electron
- Charge on the Electron
- Discovery of Protons and Neutrons
- Atomic Model
- J. J. Thomson’s Atomic Model
- Advantage and Limitations of Thomson’s Atomic Model
- Lord Rutherford’s Atomic model
- Limitations of Rutherford’s Atomic Model
- Wave Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation
- Evidence for the Quantized Electronic Energy Levels - Atomic Spectra
- Bohr’s Model for Hydrogen Atom
- Limitations of Bohr's Model
- Towards Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
- Dual Behaviour of Matter: De Broglie's relationship
- Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle
- Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
- Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom - Orbitals and Quantum Numbers
- Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom - Concept of Shells and Subshells
- Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom - Shapes of Atomic Orbitals
- Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom - Energies of Orbitals
- Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom - Filling of Orbitals in Atom
- Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom - Electronic Configuration of Atoms
- Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom - Stability of Completely Filled and Half Filled Subshells
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Concept of Chemical Bonding
- Kossel and Lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding
- Kossel-lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding - Octet Rule
- Kossel-lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding - Covalent Bond
- Lewis Structures (Lewis Representation of Simple Molecules)
- Kossel-lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding - Formal Charge
- Kossel-lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding - Limitations of the Octet Rule
- Ionic or Electrovalent Bond
- Bond Parameters
- Bond Length
- Bond Angle
- Bond Enthalpy
- Bond Order
- Resonance Structures
- Polarity of Bonds
- Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
- Valence Bond Theory
- Valence Bond Theory - Orbital Overlap Concept
- Valence Bond Theory - Directional Properties of Bonds
- Valence Bond Theory - Overlapping of Atomic Orbitals
- Valence Bond Theory - Types of Overlapping and Nature of Covalent Bonds
- Valence Bond Theory - Strength of Sigma (σ) bond and pi (π) bond
- Hybridisation
- Hybridisation - Introduction
- Types of Hybridisation
- Hybridisation of Elements Involving d Orbitals
- Molecular Orbital Theory - Introduction
- Molecular Orbital Theory
- Formation of Molecular Orbitals - Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO)
- Conditions for the Combination of Atomic Orbitals
- Types of Molecular Orbitals
- Energy Level Diagram for Molecular Orbitals
- Electronic Configuration and Molecular Behaviour
- Bonding in Some Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules
- Hydrogen Bonding - Introduction
- Hydrogen Bonding
- Cause of Formation of Hydrogen Bond
- Types of Hydrogen Bonding
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Numericals
- Electronegativity
- Shapes of Simple Molecules
- The Covalent Bond
- Elementary Idea of Metallic Bonding
- Co-ordinate Bonding
Chemical Thermodynamics
- Introduction of Thermodynamics
- Thermodynamic Terms
- The State of the System
- The Internal Energy as a State Function - Work
- The Internal Energy as a State Function - Heat
- The Internal Energy as a State Function - the General Case
- Thermodynamics Applications
- Work
- Enthalpy, H - a Useful New State Function
- Enthalpy, H - Extensive and Intensive Properties
- Enthalpy, H - Heat Capacity
- Enthalpy, H - The Relationship Between Cp and Cv for an Ideal Gas
- Measurement of ∆U and ∆H Calorimetry - ∆U Measurements
- Measurement of ∆U and ∆H Calorimetry - ∆H Measurements
- Enthalpy Change, ∆_rH of a Reaction - Reaction Enthalpy
- Standard Enthalpy of Reactions
- Enthalpy Changes During Phase Transformations
- Standard Enthalpy of Formation
- Thermochemical Equations
- Chemical Thermodynamics and Energetic
- Hess’ Law of Constant Heat Summation
- Enthalpies for Different Types of Reactions
- Standard Enthalpy of Combustion
- Enthalpy of Atomization
- Bond Enthalpy
- Lattice Enthalpy
- Enthalpy of Solution
- Enthalpy of Dilution
- Spontaneity
- Is Decrease in Enthalpy a Criterion for Spontaneity
- Entropy and Spontaneity
- Gibbs Energy and Spontaneity
- Entropy and Second Law of Thermodynamics
- Absolute Entropy and Third Law of Thermodynamics
- Gibbs Energy Change and Equilibrium
- Laws of Thermochemistry
- Basic Fundamentals of Thermodynamics
Solutions
- Introduction of Solution
- Types of Solutions
- Expressing Concentration of Solutions
- Introduction of Solubility
- Solubility
- Solubility of a Solid in a Liquid
- Solubility of a Gas in a Liquid
- Vapour Pressure of Liquid Solutions - Introduction
- Vapour Pressure of Liquid
- Vapour Pressure of Liquid- Liquid Solutions
- Raoult’s Law as a Special Case of Henry’s Law
- Vapour Pressure of Solutions of Solids in Liquids
- Ideal and Non-ideal Solutions
- Composition of Vapour Phase
- Colligative Properties and Determination of Molar Mass - Introduction
- Colligative Properties and Determination of Molar Mass
- Relative Lowering of Vapour Pressure
- Depression of Freezing Point
- Elevation of Boiling Point
- Osmosis and Osmotic Pressure
- Reverse Osmosis and Water Purification
- Abnormal Molar Masses
- Solution Numericals
- Expressing Concentration of Solutions
- Laws of Solutions
Equilibrium
- Concept of Equilibrium
- Equilibrium in Physical Processes
- Solid-liquid Equilibrium
- Liquid-vapour Equilibrium
- Solid - Vapour Equilibrium
- Equilibrium Involving Dissolution of Solid in Liquids
- Equilibrium Involving Dissolution of Gases in Liquids
- General Characteristics of Equilibria Involving Physical Processes
- Equilibrium in Chemical Processes - Dynamic Equilibrium
- Law of Chemical Equilibrium and Equilibrium Constant
- Homogeneous Equlibria
- Equilibrium Constant in Gaseous Systems
- Heterogeneous Equlibria
- Applications of Equilibrium Constants
- Predicting the Extent of a Reaction
- Predicting the Direction of the Reaction
- Calculating Equilibrium Concentrations
- Relationship Between Equilibrium Constant K, Reaction Quotient Q and Gibbs Energy G
- Factors affecting equilibrium: Le Chatelier’s principle
- Change of Concentration
- Change of Pressure
- Addition of Inert Gas
- Change of Temperature
- Effect of Catalyst
- Ionic Equilibrium in Solution
- Concept of Acid, Base, and Salt
- Acids
- Arrhenius, Bronsted-lowry and Lewis Concept of Acids and Bases
- Concept of Ionization of Acids and Bases
- Ionization of Acids and Bases
- The Ionization Constant of Water and Its Ionic Product
- Ionization Constants of Weak Acids
- Ionization of Weak Bases
- Relation Between Ka and Kb
- Di- and Polybasic Acids and Di- and Polyacidic Bases
- Factors Affecting Acid Strength
- Common Ion Effect in the Ionization of Acids and Bases
- Hydrolysis of Salts and the Ph of Their Solutions
- Buffer Solutions
- Concept of Solubility Equilibria of Sparingly Soluble Salts
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
- Introduction of Redox Reactions
- Classical Idea of Redox Reactions - Oxidation and Reduction Reactions
- Redox Reactions in Terms of Electron Transfer Reactions - Introduction
- Redox Reactions in Terms of Electron Transfer Reactions - Competitive Electron Transfer Reactions
- Oxidation Number - Introduction
- Oxidation Number
- Types of Redox Reactions
- Redox Reactions as the Basis for Titrations
- Limitations of Concept of Oxidation Number
- Balancing Redox Reactions in Terms of Loss and Gain of Electrons
- Redox Reactions and Electrode Processes
- Electrochemical Cells
- Galvanic Cells - Introduction
- Galvanic Cells - Measurement of Electrode Potential
- Relation Between Gibbs Energy Change and Emf of a Cell
- Nernst Equation - Introduction
- Nernst Equation
- Equilibrium Constant from Nernst Equation
- Electrochemical Cell and Gibbs Energy of the Reaction
- Conductance of Electrolytic Solutions - Introduction
- Conductance of Electrolytic Solutions
- Measurement of the Conductivity of Ionic Solutions
- Variation of Conductivity and Molar Conductivity with Concentration
- Electrolytic Cells and Electrolysis - Introduction
- Electrolysis
- Types of Electrolysis
- Applications of Electrolysis > Electroplating
- Products of Electrolysis
- Batteries
- Primary Batteries
- Secondary Batteries
- Fuel Cells
- Corrosion of Metals
- Different Types of Electrodes
- Conductance and Conductivity
Chemical Kinetics
- Rate of Chemical Reaction
- Rate of Reactions
- Factors Influencing Rate of a Reaction
- Elementary and Complex Reactions
- Chemical Kinetics
- Rate Law and Specific Rate Constant
- Integrated Rate Equations
- Zero Order Reactions
- First Order Reactions
- Half Life Period of a Reaction
- Pseudo First Order Reaction
- Temperature Dependence of the Rate of a Reaction
- Collision Theory of Chemical Reactions
- Effect of Catalyst on the Rate of Reaction
- Theories of Rate of Reaction
Surface Chemistry
- Surface Chemistry
- Introduction of Adsorption
- Distinction Between Adsorption and Absorption
- Adsorption
- Mechanism of Adsorption
- Adsorption from Solution Phase
- Types of Adsorption
- Adsorption Isotherms (Freundlich and Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm)
- Applications of Adsorption
- Catalysis
- Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysis
- Shape-selective Catalysis by Zeolites
- Enzyme Catalysis
- Catalysts in Industry
- Adsorption Theory of Heterogeneous Catalysis
- Colloids
- Classification of Colloids
- Classification Based on Physical State of Dispersed Phase and Dispersion Medium
- Classification Based on Nature of Interaction Between Dispersed Phase and Dispersion Medium
- Classification Based on Type of Particles of the Dispersed Phase, Multimolecular, Macromolecular and Associated Colloids
- Preparation of Colloids
- Purification of Colloidal Solutions
- Properties of Colloidal Solutions
- Emulsions
- Colloids Around Us
Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Genesis of Periodic Classification
- Modern Periodic Law and the Present Form of the Periodic Table
- Nomenclature of Elements with Atomic Number Greater than 100
- Periodic Table and Electronic Configuration
- Electronic Configurations
- The s-Block Elements
- The p-Block Elements
- The d-Block Elements (Transition Elements)
- The f-Block Elements (Inner-transition Elements)
- Metals, Non-metals and Metalloids
- Physical Properties
- Atomic Size
- Ionic Radius
- Ionization Enthalpy or Ionization Energy (IE) or Ionization Potential (IP)
- Electron Gain Enthalpy
- Electronegativity
- Periodic Trends in Chemical Properties
- Periodicity of Valence or Oxidation States
- Anomalous Properties of Second Period Elements
- Periodic Trends and Chemical Reactivity
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Numericals
- The Modern Periodic Table
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Principles and Methods of Extraction - Concentration
- Occurrence of Metals
- Basic Principles of Metallurgy > Concentration of Ores
- Types of Separation or Concentration of an Ore
- Hydraulic Washing
- Magnetic Separation
- Froth Floatation Method
- Leaching
- Extraction of Crude Metal from Concentrated Ore
- Thermodynamic Principles of Metallurgy
- Application of Thermodynamic Principles of Metallurgy
- Electrochemical Principles of Metallurgy
- Oxidation Reduction
- Refining of Crude Metals
- Uses of Aluminium, Copper, Zinc and Iron
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements Numerical
- Basic Metallurgical Processes
- Purification and Uses of Metals
Hydrogen
- Position of Hydrogen in the Periodic Table
- Hydrogen
- Dihydrogen
- Preparation of Dihydrogen
- Properties and Uses of Dihydrogen
- Hydrides
- Ionic or Saline Hydrides
- Covalent or Molecular Hydride
- Metallic or Non-stoichiometric (or Interstitial) Hydrides
- Physical Properties of Water
- Water
- Structure of Water
- Structure of Ice
- Chemical Properties of Water
- Classification of water: Soft and Hard Water
- Temporary Hardness of Water
- Permanent Hardness of Water
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- Preparation of Hydrogen Peroxide
- Physical Properties of Hydrogen Peroxide
- Structure of Hydrogen Peroxide
- Chemical Properties of Hydrogen Peroxide
- Storage of Hydrogen Peroxide
- Uses of Hydrogen Peroxide
- Heavy Water
- Dihydrogen as a Fuel
- Hydrogen as a Fuel
S-block Elements (Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals)
- Group 1 Elements - Alkali Metals
- General Characteristics of the Compounds of the Alkali Metals
- Anomalous Properties of Lithium
- Some Important Compounds of Sodium
- Group 2 Elements - Alkaline Earth Metals
- General Characteristics of the Compounds of the Alkaline Earth Metals
- Anomalous Behaviour of Beryllium
- Some Important Compounds of Calcium
- Biological Importance of Magnesium and Calcium
- Biological Importance of Sodium and Potassium
P-block Elements
- Introduction to p-block Elements
- Group 13 Elements - The Boron Family
- Boron
- Aluminum
- Some Important Compounds of Boron
- Some Important Compounds of Aluminium
- Group 14 Elements - The Carbon Family
- Important Trends and Anomalous Behaviour of Carbon
- Allotropes of Carbon > Diamond
- Allotropes of Carbon > Graphite
- Allotropes of Carbon > Fullerene
- Allotropes of Carbon > Diamond
- Some Important Compounds of Carbon and Silicon - Carbon Monoxide
- Some Important Compounds of Carbon and Silicon - Carbon Dioxide
- Some Important Compounds of Carbon and Silicon - Silicon Dioxide
- Some Important Compounds of Carbon and Silicon - Silicones
- Some Important Compounds of Carbon and Silicon - Silicates
- Some Important Compounds of Carbon and Silicon - Zeolites
- Concept of Group 15 Elements
- p-Block elements of Group 15 Elements
- Dinitrogen
- Ammonia
- Oxides of Nitrogen
- Nitric Acid
- Phosphine
- Phosphorus Halides
- Phosphorus - Allotropic Forms
- Compounds of Phosphorus
- Oxoacids of Phosphorus
- Concept of Group 16 Elements
- P - Block Group 16 Elements
- Dioxygen
- Classification of Oxides
- Simple Oxides
- Ozone
- Sulphur - Allotropic Forms
- Compounds of Sulphur
- Sulphur Dioxide
- Oxoacids of Sulphur
- Sulphuric Acid
- Concept of Group 17 Elements
- Compounds of Halogens
- P - Block Group 17 Elements
- Chlorine
- Hydrogen Chloride
- Oxoacids of Halogens
- Interhalogen Compounds
- Trends in the Acidic Nature of Hydrogen Halides
- P - Block Group 18 Elements
- Concept of Group 18 Elements
d- and f-block Elements
- General Introduction of "D" and "F" Block Element
- Position in the Periodic Table - d-block Elements
- Electronic Configurations of the D-block Elements
- General Properties of the Transition Elements (D-block)
- Some Important Compounds of Transition Elements - Oxides and Oxoanions of Metals
- F-block Elements
- The Lanthanoids
- The Actinoids
- Some Applications of d and f Block Elements
- "D" and "F" Block Elements Numericals
Co-ordination Compounds
- Introduction of Coordination Compounds
- Werner’s Theory of Coordination Compounds
- Definitions of Some Important Terms Pertaining to Coordination Compounds
- Nomenclature of Coordination Compounds - Formulas of Mononuclear Coordination Entities
- Nomenclature of Coordination Compounds - Naming of Mononuclear Coordination Compounds
- Isomerism in Coordination Compounds
- Isomerism in Coordination Compounds
- Stereoisomerism
- Structural Isomerism
- Bonding in Coordination Compounds - Introduction
- Bonding in Coordination Compounds
- Valence Bond Theory (VBT)
- Magnetic Properties of Coordination Compounds
- Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
- Colour in Coordination Compounds
- Bonding in Metal Carbonyls
- Stability of Coordination Compounds
- Importance and Applications of Coordination Compounds
- Coordination Compounds Numerical
- Organo Metallic Compounds
- Magnetic Moment of a Coil
- Coordination Number
Environmental Chemistry
- Atmospheric Pollution
- Tropospheric Pollution - Gaseous Air Pollutants
- Tropospheric Pollution - Particulate Pollutants
- Stratospheric Pollution
- International Standards for Drinking Water
- Soil Pollution
- Industrial Waste
- Strategies to Control Environmental Pollution
- Green Chemistry - Introduction
- Green Chemistry in Day-to-day Life
Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds
- Introduction of Methods of Purification of Organic Compounds
- Purification of Solids
- Sublimation
- Crystallisation Method
- Simple Distillation Method
- Fractional Distillation Method
- Distillation Under Reduced Pressure (Vacuum Distillation)
- Steam Distillation
- Solvent Extraction (Using a Separating Funnel Method)
- Chromatography Method
- Chromatography Method > Adsorption Chromatography
- Chromatography Method > Partition Chromatography
- Qualitative Analysis of Organic Compounds - Detection of Carbon and Hydrogen
- Qualitative Analysis of Organic Compounds - Detection of Other Elements
- Quantitative Analysis of Carbon and Hydrogen
- Quantitative Analysis of Nitrogen
- Quantitative Analysis of Halogens
- Quantitative Analysis of Sulphur
- Quantitative Analysis of Phosphorus
- Quantitative Analysis of Oxygen
- Empirical Formula and Molecular Formula
Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
- Tetravalence of Carbon - Shapes of Organic Compounds
- Organic Compounds
- Complete, Condensed and Bond-line Structural Formulas
- Three-dimensional Representation of Organic Molecules
- Classification of Organic Compounds
- Nomenclature
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Alkanes
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds Having Functional Group(s)
- Nomenclature of Substituted Benzene Compounds
- Isomerism
- Fundamental Concepts in Organic Reaction Mechanism
- Fission of a Covalent Bond
- Nucleophiles and Electrophiles
- Electron Movement in Organic Reactions
- Electron Displacement Effects in Covalent Bonds
- Inductive Effect
- Resonance Structure
- Resonance Effect
- Electromeric Effect (E Effect)
- Hyperconjugation
- Types of Organic Reactions and Mechanisms
Hydrocarbons
- Classification of Hydrocarbons
- Alkanes - Introduction
- Alkanes
- Nomenclature and Isomerism
- Preparation of Alkanes from Unsaturated Hydrocarbons, Alkyl Halides and Carboxylic Acids
- Conformations (Ethane)
- Mechanism of Halogenation of Alkane
- Physical Properties of Alkanes
- Chemical Properties of Alkanes
- Alkenes
- Structure of Double Bond (Ethene)
- Nomenclature
- Preparation of Alkenes from Alkynes, Alkyl Halides, Vicinal Dihalides and Alcohols by Acidic Dehydration
- Isomerism
- Physical Properties of Alkenes
- Chemical Properties of Alkenes
- Alkynes
- Alkynes
- Nomenclature and Isomerism
- Structure of Triple Bond
- Preparation of Alkynes from Calcium Carbide and Vicinal Dihalides
- Physical Properties of Alkynes
- Chemical Properties of Alkynes
- Aromatic Hydrocarbons
- Nomenclature and Isomerism
- Structure of Benzene
- Aromaticity (Huckel Rule)
- Preparation of Benzene
- Electrophilic Substitution Reactions
- Mechanism of Electrophilic Substitution Reactions
- Directive Influence of a Functional Group in Monosubstituted Benzene
- Physical Properties of Aromatic Hydrocarbons
- Chemical Properties of Aromatic Hydrocarbons
- Carcinogenicity and Toxicity
Organic Compounds Containing Halogens
- Introduction of Organic Compounds Containing Halogens
- Introduction to Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Nomenclature
- Nature of C-X Bond
- Classification of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Methods of Preparation of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Physical Properties of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Hydrocarbons: Alkanes
- Reactions of Haloalkanes - Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
- Reactions of Haloalkanes - Elimination Reactions
- Reactions of Haloalkanes - Reaction with Metals
- Reactions of Haloarenes - Nucleophilic Substitution
- Reactions of Haloarenes - Electrophilic Substitution Reactions
- Reactions of Haloarenes - Reaction with Metals
- Polyhalogen Compounds
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Numericals
Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen
- Introduction of Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
- Classification of Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
- Nomenclature of Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
- Structures of Functional Groups of Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
- Identification of Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Alcohols
- Methods of Preparation of Alcohols
- Methods of Preparation of Phenols
- Physical and Chemical Properties of Alcohols and Phenols
- Chemical Reactions of Alcohols and Phenols
- Reactions Involving Cleavage of O-H Bond
- Reactions Involving Cleavage of Carbon–Oxygen (C–O) Bond in Alcohols
- Reactions of Phenols
- Preparation of Commercially Important Alcohols
- Preparation of Ethers
- Physical Properties of Ethers
- Chemical Reaction of Ethers - Cleavege of C-O Bonds
- Chemical Reaction of Ethers - Electrophilic Substitution
- Aldehydes and Ketones
- Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones
- Structure of the Carbonyl Group
- Preparation of Aldehydes
- Preparation of Ketones
- Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones
- Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones
- Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
- Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Reduction
- Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Oxidation
- Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Reactions Due to α-hydrogen
- Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Other Reactions
- Relative Reactivities of Aldehydes and Ketones
- Uses of Aldehydes and Ketones
- Carboxylic Acids
- Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids
- Structure of the Carboxyl group
- Methods of Preparation of Carboxylic Acids
- Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids
- Chemical Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Reactions Involving Cleavege of O-H Bond
- Chemical Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Reactions Involving Cleavege of C-OH Bond
- Chemical Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Reactions Involving –COOH Group
- Chemical Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Substitution Reactions in the Hydrocarbon Part
- Uses of Carboxylic Acids
Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Introduction of Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Structure of Amines
- Classification of Amines
- Amines
- Nomenclature of Animes
- Preparation of Amines
- Chemical Reactions of Amines - Basic Character of Amines
- Chemical Reactions of Amines - Alkylation and Acylation
- Chemical Reactions of Amines - Carbylamine Reaction
- Chemical Reactions of Amines - Reaction with Nitrous Acid
- Chemical Reactions of Amines - Reaction with Arylsulphonyl Chloride
- Chemical Reactions of Amines - Electrophilic Substitution
- Uses of Amines
- Identification of Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Amines
- Physical Properties of Amines
- Introduction of Diazonium Salts
- Diazonium Salts
- Method of Preparation of Diazonium Salts
- Chemical Reaction of Diazonium Salts - Reactions Involving Displacement of Nitrogen
- Chemical Reaction of Diazonium Salts - Reactions Involving Retention of Diazo Group
- Importance of Diazonium Salts in Synthesis of Aromatic Compounds
- Physical Properties of Diazonium Salts
- Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Numericals
- Amides, Cyanides and Lsocyanldes
- Nitrocompounds, Alkyl Nitrites and Diazonium Salts
Polymers
- Introduction to Polymers
- Preparation of Polymers
- Classification of Polymers Based on Source
- Classification of Polymers Based on Structure
- Classification of Polymers Based on Mode of Polymerisation
- Classification of Polymers Based on Molecular Forces
- Some Important Polymers
- Types of Polymerisation Reactions - Addition Polymerisation or Chain Growth Polymerisation
- Types of Polymerisation Reactions - Condensation Polymerisation Or Step Growth Polymerisation
- Types of Polymerisation Reactions - Copolymerisation
- Types of Polymerisation Reactions - Rubber
- Molecular Mass of Polymers
- Properties of Polymers
- Biodegradable Polymers
- Polymers of Commercial Importance
- Uses of Polymers
- Polymers Numericals
Biomolecules
- Biomolecules
- Introduction of Carbohydrates
- Classification of Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates
- Monosaccahrides
- Preparation of Glucose
- Structures of Glucose
- Structure of Fructose
- Disaccharides - Sucrose, Maltose and Lactose
- Polysaccharides - Starch, Cellulose and Glycogen
- Importance of Carbohydrates
- Introduction of Proteins
- Proteins
- Amino Acids
- Classification of Amino Acids
- Structure of Proteins
- Denaturation of Proteins
- Peptide
- Lipids and Hormones
- Introduction of Enzymes
- Mechanism of Enzyme Action
- Introduction of Vitamins
- Vitamins
- Classification of Vitamins
- Introduction of Nucleic Acids
- Chemical Composition of Nucleic Acids
- Structure of Nucleic Acids
- Biological Functions of Nucleic Acids
- Biomolecules Numericals
Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Classification of Drugs
- Drug-target Interaction - Enzymes as Drug Targets
- Drug-target Interaction - Receptors as Drug Targets
- Therapeutic Action of Different Classes of Drugs - Antacids
- Therapeutic Action of Different Classes of Drugs - Antihistamines
- Therapeutic Action of Different Classes of Drugs - Neurologically Active Drugs
- Therapeutic Action of Different Classes of Drugs - Antimicrobials
- Therapeutic Action of Different Classes of Drugs - Antifertility Drugs
- Chemicals in Food - Artificial Sweetening Agents and Food Preservatives
- Cleansing Agents - Soaps
- Cleansing Agents - Synthetic Detergents
- Chemistry in Everyday Life Numericals
- Three States of Matter
- Comparison of Solids, Liquids, and Gases
Three States of Matter
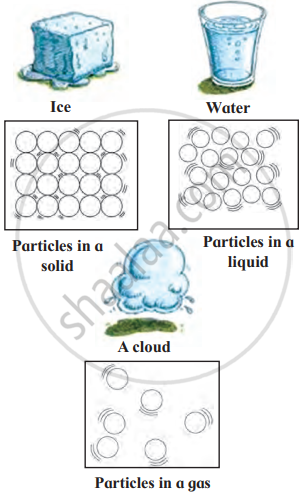
1. The Solid State: Solids have a definite shape and fixed size. The particles in solids are packed tightly together, which is why solids are usually hard and firm. Solids cannot be easily compressed or squashed because there is no space between the particles.
Example of Solids:
- Ice is a solid form of water, and it has a definite shape.
- Other examples include wood, stone, pencils, and books.
2. The Liquid State: Liquids do not have a definite shape, but they do have a fixed volume. The particles in a liquid are more loosely arranged than in a solid, which allows liquids to flow and take the shape of the container they are in. Liquids are not easily compressed, as the particles are still fairly close together.
Example of Liquids:
- Water is a liquid. It flows and takes the shape of any container, like a glass or bottle.
- Other examples of liquids include milk, juice, and oil.
3. The Gaseous State: Gases do not have a definite shape or a fixed volume. They will spread out and fill any space they are in. The particles in gases are very far apart and move around freely in all directions. Gases can be easily compressed because there is a lot of space between the particles.
Example of Gases:
- Air is a mixture of gases, including oxygen and nitrogen. You cannot see air, but it fills the space around us.
- Other examples include steam, carbon dioxide, and helium (which is used in balloons).
Comparison of Solids, Liquids, and Gases
| Points | Solids | Liquids | Gases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example | A piece of iron | Water, spirit, oil | Air |
| Shape | Has a shape of its own. Retains shape, no matter how it is kept. | Does not have a shape of its own. Takes the shape of the container. | Does not have a shape of its own. Occupies all the available space. |
| Volume | Has a definite volume. Solids like sugar and sand, when poured on a flat surface, form a heap. | Has a specific volume. Occupies a definite portion of a container. Spreads on a flat surface on pouring. Flows downwards along a slope. | Does not have a definite volume. On changing the pressure on a gas in a closed container, its volume also changes. |
