Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is myopia?
Advertisements
Solution
Myopia or near-sightedness is the defect of vision in which a human eye can see nearby objects distinctly but is unable to see distant objects clearly. In this case, the image of a distant object is formed in front of the retina instead of on the retina.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the importance of ciliary muscles in the human eye. Name the defect of vision that arises due to gradual weakening of the ciliary muscles. What types of lenses are required by the person suffering from this defect to see the objects clearly?
Akshay, sitting in the last row in his class, could not see clearly the words write on the blackboard. When the teacher noticed it, he announced if any student sitting in the front row could volunteer to exchange his seat with Akshay. Salman immediately agreed to exchange his seat with Akshay. He could now see the words written on the blackboard clearly. The teacher thought it fit to send the message to Akshay’s parents advising them to get his eyesight checked.
In the context of the above event, answer the following questions:-
(a) Which defect of vision is Akshay suffering from? Which type of lens is used to correct this defect?
(b) State the values displayed by the teacher and Salman.
(c) In your opinion, in what way can Akshay express his gratitude towards the teacher and Salman?
Millions of people in the developing countries of the world are suffering from corneal blindness. These persons can be cured by replacing the defective cornea with the cornea of a donated eye. A charitable society of your city has organised a campaign in your neighbourhood in order to create awareness about this fact. If you are asked to participate in this mission, how would you contribute in this noble cause?
(i) State the objective of organising such campaigns.
(ii) List two arguments which you would give to motivate the people to donate their eyes after death.
(iii) List two values which are developed in the persons who actively participate and contribute in such programmes.
List three common refractive defects of vision. Suggest the way of correcting these defects.
What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision?
Name the defect of vision in a person:
whose near point is more than 25 on away.
Name the defect of vision in a person:
whose far point is less than infinity
Name any two defects of vision which can be corrected by using spectacles.
Where is the near point of a person suffering from hypermetropia (or long-sightedness)?
A man can read the number of a distant but clearly but he finds difficulty in reading a book.
From which defect of the eye is he suffering?
A student sitting in the last row of the class-room is not able to read clearly the writing on the blackboard.
How can this defect by corrected?
Differentiate between myopia and hypermetropia. What type of spectacles should be worn by a person having the defects of myopia as well as hypermetropia? How does it help?
The defect of vision which cannot be corrected by using spectacles is:
(a) myopia
(b) presbyopia
(c) cataract
(d) hypermetropia
The picture given here shows a person wearing 'half-moon' spectacles. What sort of eye-defect do do you think he has? Why are these particular spectacles useful to him?
A short-sighted person has a near point of 15 cm and a far point of 40 cm.
(a) Can he see clearly an object at a distance of:
(i) 5 cm?
(ii) 25 cm?
(iii) 50 cm?
(b) To see clearly an object at infinity, what kind of spectacle lenses does he need?
A person can read a book clearly only if he holds it at an arm's length from him. Name the defect of vision:
if the person is a young man
Which part of the eye is grafted in a needy patient from a donated eye?
By closing the eyes and gently pressing them by your palms, you may see some specks of brilliant light. How do you get this sensation while there is no light entering your eyes?
Have a look at the posture of this girl who is reading a book and answer the questions which follow:

Name the problem she is facing.
Distinguish between the following pair of words:
Myopia and hypermetropia
Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye? Study the same and answer the question that follow:
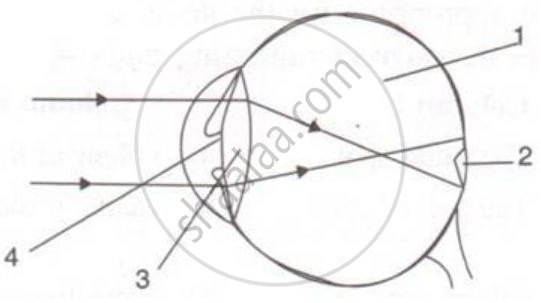
Give two possible reasons for this defect of the eye in human beings.
Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye? Study the same and answer the question that follow:

Name the parts labeled 1 to 4.
Have a look at the posture of this woman who is reading a book and answer the questions which follow:

What are the two conditions shown in sections A and B of the eye as applicable to her?
Anuja cannot see the blackboard writing but she can see nearby things.
(a) What is the eye defect she is suffering from?
(b) State the possible reason for her defect.
(c) How is it corrected
The near point of the eye of a person is 50 cm. Find the nature and power of the corrective lens required by the person to enable him to see clearly the objects placed at 25 cm from the eye?
Give Reason:
Older people require glasses to read and write.
Differentiate between:
Myopia and Hypermetropia.
Given below is a diagrammatic representation of a defect of the human eye:

(i) Identify the defect.
(ii) Mention two reasons for the above defect.
(iii) State how the defect can be rectified.
(iv) Name the part of the eye responsible for maintaining the shape of the eyeball.
With respect to human eye explain:
(i) How is the image formed on the retina?
(ii) How is the amount of light entering the eye-controlled?
(iii) What type of lens is used for the correction of ‘Long sight’ defect?
(iv) With the help of a ray, diagram show the defect of the eye and then its correction after the use of a lens.
Nearsightedness : concave lens : : farsightedness : _______
Given below is a diagram showing a defect of vision. Name the defect of vision and draw an accurately labelled diagram to correct this defect.

A person cannot see distinctly objects kept beyond 2 m. This defect can be corrected by using a lens of power:
When do we consider a person to be myopic or hypermetropic? Explain using diagrams how the defects associated with myopic and hypermetropic eye can be corrected?
Correlate the given sequence:
Hypermetropia : Convex lens : ______ : Concave lens
Observe the figure and answer the following questions:

- Name the defect of vision represented in the above figure.
- State the reasons for this defect.
- How is it corrected?
- Draw the diagram to show the correction of this defect.
A person is unable to see clearly a poster fixed on a distant wall. He however sees it clearly when standing at a distance of about 2 m from the wall.
- Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image by his eye lens when he is far away from the wall.
- List two possible reasons of this defect of vision.
- Draw ray diagram to show the correction of this defect using appropriate lens.
Name the following:
Two kinds of accomodations.
