Topics
Force, Work, Power and Energy
Force
Light
Work, Energy and Power
- Concept of Work
- Measurement of Work
- Expression for Work (W = F S cosθ)
- Work Done by the Force of Gravity (W = mgh)
- Concept of Power
- Work vs Power
- Concept of Energy
- Energy vs Power
- Mechanical Energy > Potential Energy (U)
- Mechanical Energy > Kinetic Energy (K)
- Potential vs Kinetic Energy
- Conversion of Potential Energy into Kinetic Energy
- Forms of Energy > Solar Energy
- Forms of Energy > Heat Energy
- Forms of Energy > Light Energy
- Forms of Energy > Chemical Energy
- Forms of Energy > Hydro Energy
- Forms of Energy > Electrical Energy
- Forms of Energy > Nuclear Energy
- Forms of Energy > Geo Thermal Energy
- Forms of Energy > Wind Energy
- Forms of Energy > Sound Energy
- Forms of Energy > Magnetic Energy
- Forms of Energy > Mechanical Energy
- Conversion of Energies
- Principle of Conservation of Energy
- Proof: Kinetic + Potential Energy = Constant for Free Fall
- Application of the Principle of Conservation of Energy
Sound
Machines
- Concept of Machines
- Technical Terms Related to a Machine
- Principle of a Machine
- Efficiency, Mechanical Advantage, and Velocity Ratio
- Levers
- Types of Levers
- Pulley
- Single Fixed Pulley
- A Single Movable Pulley
- Single Pulley vs Single Movable Pulley
- Combination of Pulleys
- Using one fixed pulley and other movable pulleys
- Using several pulleys in two blocks (block and tackle system)
Electricity and Magnetism
Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
- Light: Reflection and Refraction
- Refraction of Light
- Laws of Refraction
- Speed of Light in Different Media
- Principle of Reversibility of the Path of Light
- Refraction Laws & Glass Index
- Refraction of Light Through a Rectangular Glass Block
- Multiple Images in a Thick Mirror
- Prism
- Refraction of Light Through a Prism
- Real and Apparent Depth
- Apparent Bending of a Stick Under Water
- Consequences of Refraction of Light
- Transmission of Light From a Denser Medium to a Rarer Medium
- Critical Angle
- Relationship between Critical Angle and Refractive Index
- Total Internal Reflection
- Total Internal Reflection in a Prism
- Total Internal Reflection Through a Right-Angled Isosceles Prism
- Total Internal Reflection Through an Equilateral Prism
- Total Internal Reflection Through Right-angled prism
- Use of a Total Internal Reflecting Prism in Place of a Plane Mirror
- Total Internal Reflection vs Reflecting from a Plane Mirror
- Consequences of Total Internal Refraction
Heat
Refraction Through a Lens
- Concept of Lenses
- Action of a Lens as a Set of Prisms
- Technical Terms Related to a Lens
- Convex Lens vs Concave Lens
- Refraction of Light Through an Equi-Convex Lens and an Equi-Concave Lens
- Principal Rays for Ray Diagrams
- Real Image vs Virtual Image
- Construction of a Ray Diagram for a Lens
- Images Formed by Convex Lenses
- Images Formed by Concave Lenses
- Sign Convention
- Lens Formula
- Linear Magnification
- Power of a Lens
- Magnifying Glass Or Simple Microscope
- Application of Lenses
- Experimental Determination of Focal Length of Convex Lens
- Convex Lens vs Concave Lens
Modern Physics
Spectrum
- Deviation Produced by a Triangular Prism
- Colour in White Light with Their Wavelength and Frequency Range
- Dispersion of Light
- Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Properties and Uses of Different Radiations of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Distinction between Ultraviolet, Visible, and Infrared Radiations
- Scattering of Light
- Applications of Scattering of Light
Sound
- Sound Waves
- Light Waves vs Sound Waves
- Reflection of Sound Waves
- Echo
- Determination of Speed of Sound by the Method of Echo
- Use of Echoes
- Natural Vibrations
- Damped Vibrations
- Natural Vibrations vs Damped Vibrations
- Forced Vibrations
- Natural Vibrations vs Forced Vibrations
- Resonance (a special case of forced vibrations)
- Demonstration of Resonance
- Forced Vibrations vs Resonant Vibrations
- Examples of Resonance
- Characteristics of Sound
- Loudness and Intensity
- Pitch and frequency
- Quality and Wave Form
- Music and Noise
Current Electricity
- Electric Charge
- Electric Current
- Potential and Potential Difference
- Electric Resistance
- Ohm's Law
- Experimental Verification of Ohm’s Law
- Ohmic and Non-ohmic Resistors
- Specific Resistance
- Choice of Material of a Wire
- Superconductors
- Electro-Motive Force of a Cell
- Terminal Voltage of a Cell
- Internal Resistance of a Cell
- Resistance of a System of Resistors
- Resistors in Series
- Resistors in Parallel
- A combination of resistors in both series and parallel
- Forms of Energy > Electrical Energy
- Measurement of Electrical Energy
- Electrical Power
- Commercial Unit of Electrical Energy
- Power Rating of Common Electrical Appliances
- Household Consumption of Electric Energy
- Heating Effect of Electric Current
Household Circuits
- Transmission of Power from the Power Generating Station to the Consumer
- Power Distribution to a House
- House Wiring (Ring System)
- Fuse
- Reason for connecting the fuse in the live wire
- Current Rating of a Fuse
- Switches
- Circuits with Dual Control Switches (Staircase Wire)
- Earthing
- Three-pin Plug and Socket
- Colour Coding of Wires in a Cable
- High Tension Wires
- Precautions to Be Taken While Using Electricity
Electro-Magnetism
- Oersted's Experiment
- Applications of Biot-Savart's Law > Magnetic Field due to a Finite Straight Current-Carrying Wire
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Applications of Biot-Savart's Law > Magnetic Field at the Centre of a Circular Loop
- Applications of Ampere’s Circuital Law > Magnetic Field of a Long Straight Solenoid
- Electromagnet
- Permanent Magnet
- Comparison of an Electro Magnet with a Permanent Magnet
- Advantages of an Electromagnet over a Permanent Magnet
- Uses of Electromagnet
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Simple D.C. Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Demonstration of the Phenomenon of Electromagnetic Induction
- Faraday's Explanation
- Faraday's Laws of Electromagnetic Induction
- A.C. Generator
- Frequency of an a.c. in Household Supplies
- Comparison Between A.C. Generator and D.C. Motor
- Transformers
Calorimetry
- Heat
- The Temperature and a Thermometer
- Factors Affecting the Quantity of Heat Absorbed to Increase the Temperature of a Body
- Heat vs Temperature
- Thermal or Heat Capacity
- Specific Heat Capacity
- Heat Capacity vs Specific Heat Capacity
- Specific Heat Capacity of Some Common Substances
- Calorimetry
- Principle of Method of Mixtures or Principle of Calorimetry
- Natural Phenomena and Consequences of High Specific Heat Capacity of Water
- Examples of High and Low Heat Capacity
- Change of State
- Melting and Freezing
- Melting Point and Its Effects
- Vaporisation or Boiling
- Boiling Point and Its Effects
- Latent Heat
- Specific Latent Heat of Fusion of Ice
- Explanation of Latent Heat of Melting based on Kinetic Model
- Natural Consequences of High Specific Latent Heat of Fusion of Ice
Radioactivity
- Structure of the Atom and Nucleus
- Atomic Model
- Isotopes
- Isobars
- Isotones
- Radioactivity
- Radioactivity as emission of Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Radiations
- Properties of Alpha Particles
- Properties of Beta Particles
- Properties of Gamma Radiations
- Distinction between the Properties of α, β, and γ Radiations
- Changes Within the Nucleus in Alpha, Beta and Gamma Emission
- Uses of Radioactive Isotopes
- Sources of Harmful Radiations
- Harmful Effects of Radiation
- Safety Precautions While Using Nuclear Energy
- Background Radiations
- Forms of Energy > Nuclear Energy
- Nuclear Fission
- Radioactive Decay Vs Nuclear Fission
- Nuclear Fusion
- Nuclear Fission Vs Nuclear Fusion
- Definition: Pitch
Experiment
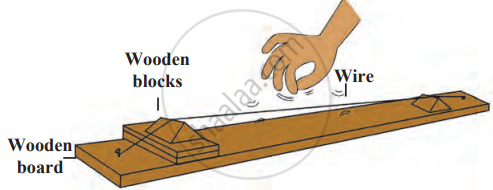
1. Aim: To observe how tension in a wire affects the pitch and frequency of the sound produced.
2. Requirements: wooden board (80-90 cm long, 5 cm wide), two nails, thin metal wire, wedge-shaped wooden or plastic block, small rectangular blocks, hammer.
3. Procedure
- Hammer the nails into the wooden board near its two ends.
- Tie the metal wire tightly between the two nails.
- Place the wedge-shaped block under the wire near each nail.
- Pluck the wire lightly and observe if you hear sound and see vibration.
- Now add two or three small blocks under one wedge without changing the length of the wire.
- Observe the change in tension in the wire and pluck it again.
- Listen to the sound and note the difference in pitch and frequency.
4. Conclusion: Increased tension in the wire produces a higher frequency and the sound becomes shriller (higher pitch). Reduced tension produces a lower frequency and the sound becomes less shrill (lower pitch). This experiment shows that pitch depends on the frequency: a higher frequency creates a higher pitch, and a lower frequency creates a lower pitch.
The pitch of a sound
Definition: Pitch
Pitch is that characteristic of sound by which an acute (or shrill) note can be distinguished from a grave (or flat) note of the same loudness and quality.
