Topics
Living World
- What is ‘Living’?
- Taxonomical Aids
Systematics of Living Organisms
- Systematics of Living Organisms (Introduction)
- Systematics of Living Organisms (Introduction)
- Concept of Systematics
- Concept of Systematics
- Classification of Taxonomy
- Classification of Taxonomy
- Three Domains of Life
- Three Domains of Life
- Chemotaxonomy
- Chemotaxonomy
- Numerical Taxonomy
- Numerical Taxonomy
- Cladogram
- Cladogram
- Phylogeny
- Phylogeny
- DNA Barcoding
- DNA Barcoding
- Taxonomic Hierarchy of Living Organisms: Unit of Classification
- Taxonomic Hierarchy of Living Organisms: Unit of Classification
- Taxonomic Hierarchy
- Taxonomic Hierarchy
- Units of Classification
- Units of Classification
- Binomial Nomenclature
- Salient Features of Five Kingdoms
- Salient Features of Five Kingdoms
- Acellular Organisms
- Acellular Organisms
Kingdom Plantae
- Classification of Kingdom Plantae
- Salient Features of Major Plant Groups Under Cryptogams
- Salient Features of Major Plant Groups Under Phanerogams
- Plant Life Cycle and Alternation of Generations
Kingdom Animalia
- Criteria Used for Animal Classification
- Animal Body Plan
- Animal Classification
Cell Structure and Organization
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- Types of Cells
- Components of Eukaryotic Cell
Biomolecules
- Biomolecules in Living System
- Biomolecules in the Cell
- Biomolecules in the Cell > Carbohydrates
- Biomolecules in the Cell > Lipids
- Biomolecules in the Cell > Proteins
- Biomolecules in the Cell > Nucleic Acids
- Biomolecules in the Cell > Enzymes
- Nature of Enzyme Action
- Nomenclature of Enzymes
- Classification of Enzymes
- Mechanism of Enzyme Action
- Enzyme - Substrate Interactions
- Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
- Metabolism
- Metabolic Pool
- Secondary metabolites (SMs)
Cell Division
Plant Tissues and Anatomy
- Tissues - “The Teams of Workers”
- Meristems or Meristematic Tissues
- Permanent Tissue
- Tissue System
- Secondary Growth in Plants
- Wood
- Cork Cambium and Secondary Growth
- Anatomy of Root, Stem and Leaf
Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Phanerogams > Division II- Angiosperms
- Morphology
- Study of Some Important Families
Animal Tissue
Study of Animal Type : Cockroach
- Habit and Habitat
- Systematic Position
- External Morphology
- Body Cavity
- Digestive System of Cockroach
- Circulatory System Or Blood Vascular System
- Human Respiratory System
- Reproduction System
- Interactions with Mankind
Photosynthesis
- Concept of Photosynthesis
- Chloroplasts
- Nature of Light
- Mechanism of Photosynthesis
- Light-Dependent Phase of Photosynthesis
- Photophosphorylation
- Light-Independent Phase of Photosynthesis
- Photorespiration
- C4 Pathway Or Hatch-slack Pathway
- Cam - Crassulacean Acid Metabolism
- Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Respiration and Energy Transfer
- Production of ATP
- Cellular Respiration
- Phases of Respiration: Glycolysis
- Phases of Respiration: Pyruvate Oxidation (Link Reaction)
- Phases of Respiration: Electron Transport System (Ets) and Oxidative Phosphorylation
- Phases of Respiration: Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle or Kreb’s Cycle)
- Phases of Respiration: Electron Transport Chain (Electron Transfer System)
- Phases of Respiration: Fermentation
- Respiratory Balance Sheet
- Amphibolic Pathways
- Utility of Stepwise Oxidation
- Respiratory Quotient (R.Q.)
Human Nutrition
- Nutrients and Nutrition
- Component of Food
- Human Digestive System
- The Mouth and Buccal Cavity
- The Salivary Glands
- The Teeth and Its Structure
- Tongue
- The Food Pipe/Oesophagus
- The Stomach
- The Small Intestine
- Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
- The Large Intestine
- Liver
- Physiology of Digestion
- Absorption of Food
- Assimilation of Food
- Egestion of Food
- Nutritional and Digestive Tract Disorders
Excretion and Osmoregulation
- Excretion
- Modes of Excretion: Ammonotelism, Ureotelism, and Uricotelism
- Human Excretory System
- Kidney and Its Internal Structure
- Structure of a Kidney Tubule (Nephrons)
- Function of the Kidney - “Production of Urine”
- Concentration of Urine
- Composition of Urine
- The Excretory Organs
- Common Disorders of the Urinary System
Skeleton and Movement
- Movements and Locomotion
- Location and Structure of Skeletal Muscles
- Working of Skeletal Muscles
- Mechanism of Muscle Contraction
- Physiology of Muscle Relaxation
- Relaxation of Muscle Fibres
- Skeletal System
- Group of Skeleton
- Types of Joints
- Disorders Related to Muscles
- Disorders Related to Bones
- Introduction
- Types of Muscular Tissue
Maharashtra State Board: Class 9
Introduction:
Muscular tissue is a specialised type of tissue responsible for bodily movements through contraction and relaxation. It is composed of long, tube-shaped cells called muscle fibres, which contain fine fibrils known as myofibrils. These fibrils are made up of contractile proteins that enable the muscles to contract and relax during movement. Found in various parts of the body, muscular tissue is essential for both voluntary and involuntary movements.
There are three main types of muscular tissues:
- Skeletal muscles, which enable voluntary movements
- Smooth muscles, which control involuntary actions
- Cardiac muscles, which are responsible for the rhythmic contractions of the heart.
Maharashtra State Board: Class 9
Types of Muscular Tissue:
| Feature | Striated Muscles (Skeletal) | Non-Striated Muscles (Smooth) | Cardiac Muscles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Long, cylindrical, multinucleate, no branches. | Short, spindle-shaped, uninucleate, no branches. | Cylindrical, uninucleate, branched. |
| Bands | Alternate dark and light bands are present. | Dark and light bands are absent. | Dark and light bands are present. |
| Control | Voluntary (under our will). | Involuntary (not under our will). | Involuntary (not under our will). |
| Location | Attached to bones. | Walls of alimentary canal, blood vessels, etc. | Walls of the heart. |
| Diagram | 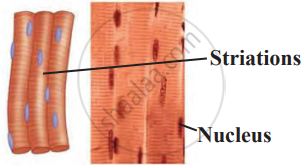 |
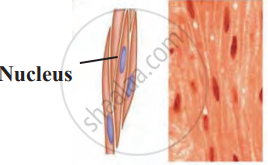 |
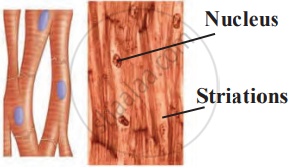 |
| Function | Movements like running, speaking, etc. | Movements like eyelid motion, passage of food, and contraction of blood vessels. | Rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart. |
